MongoDB and Python |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › mongdb python › MongoDB and Python |
MongoDB and Python
|
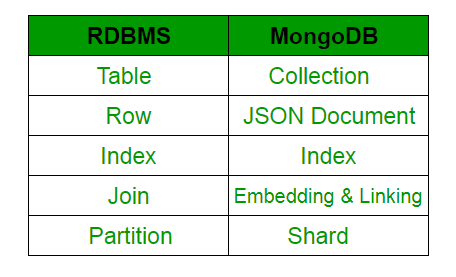
Prerequisite : MongoDB : An introductionMongoDB is a cross-platform, document-oriented database that works on the concept of collections and documents. MongoDB offers high speed, high availability, and high scalability.The next question which arises in the mind of the people is “Why MongoDB”?Reasons to opt for MongoDB : It supports hierarchical data structure (Please refer docs for details)It supports associate arrays like Dictionaries in Python.Built-in Python drivers to connect python-application with Database. Example- PyMongoIt is designed for Big Data.Deployment of MongoDB is very easy.MongoDB vs RDBMS
MongoDB and PyMongo Installation Guide First start MongoDB from command prompt using :Method 1:mongodorMethod 2: net start MongoDB
After this, connect to the default host and port. Connection to the host and port is done explicitly. The following command is used to connect the MongoClient on the localhost which runs on port number 27017. client = MongoClient(‘host’, port_number)example:- client = MongoClient(‘localhost’, 27017)It can also be done using the following command: client = MongoClient(“mongodb://localhost:27017/”)Access DataBase Objects : To create a database or switch to an existing database we use:Method 1 : Dictionary-stylemydatabase = client[‘name_of_the_database’]Method2 : mydatabase = client.name_of_the_databaseIf there is no previously created database with this name, MongoDB will implicitly create one for the user.Note : The name of the database fill won’t tolerate any dash (-) used in it. The names like my-Table will raise an error. So, underscore are permitted to use in the name. Accessing the Collection : Collections are equivalent to Tables in RDBMS. We access a collection in PyMongo in the same way as we access the Tables in the RDBMS. To access the table, say table name “myTable” of the database, say “mydatabase”.Method 1:mycollection = mydatabase[‘myTable’]Method 2 : mycollection = mydatabase.myTable>MongoDB store the database in the form of dictionaries as shown:> record = { title: 'MongoDB and Python', description: 'MongoDB is no SQL database', tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'], viewers: 104 }‘_id’ is the special key which get automatically added if the programmer forgets to add explicitly. _id is the 12 bytes hexadecimal number which assures the uniqueness of every inserted document. We normally use insert_one() method document into our collections. Say, we wish to enter the data named as record into the ’myTable’ of ‘mydatabase’. rec = myTable.insert_one(record)The whole code looks likes this when needs to be implemented. # importing modulefrom pymongo import MongoClient # creation of MongoClientclient=MongoClient() # Connect with the portnumber and hostclient = MongoClient(“mongodb://localhost:27017/”) # Access databasemydatabase = client[‘name_of_the_database’] # Access collection of the databasemycollection=mydatabase[‘myTable’] # dictionary to be added in the databaserec={title: 'MongoDB and Python', description: 'MongoDB is no SQL database', tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'], viewers: 104 } # inserting the data in the databaserec = mydatabase.myTable.insert(record)Querying in MongoDB : There are certain query functions which are used to filter the data in the database. The two most commonly used functions are:find()find() is used to get more than one single document as a result of query.for i in mydatabase.myTable.find({title: 'MongoDB and Python'}) print(i)This will output all the documents in the myTable of mydatabase whose title is ‘MongoDB and Python’. count()count() is used to get the numbers of documents with the name as passed in the parameters.print(mydatabase.myTable.count({title: 'MongoDB and Python'}))This will output the numbers of documents in the myTable of mydatabase whose title is ‘MongoDB and Python’. These two query functions can be summed to give a give the most filtered result as shown below. print(mydatabase.myTable.find({title: 'MongoDB and Python'}).count())To print all the documents/entries inside ‘myTable’ of database ‘mydatabase’ : Use the following code:from pymongo import MongoClient try: conn = MongoClient() print("Connected successfully!!!")except: print("Could not connect to MongoDB") # database name: mydatabasedb = conn.mydatabase # Created or Switched to collection names: myTablecollection = db.myTable # To find() all the entries inside collection name 'myTable'cursor = collection.find()for record in cursor: print(record)This article is contributed by Rishabh Bansal and Shaurya Uppal. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using contribute.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to [email protected]. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks. Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above. |
【本文地址】
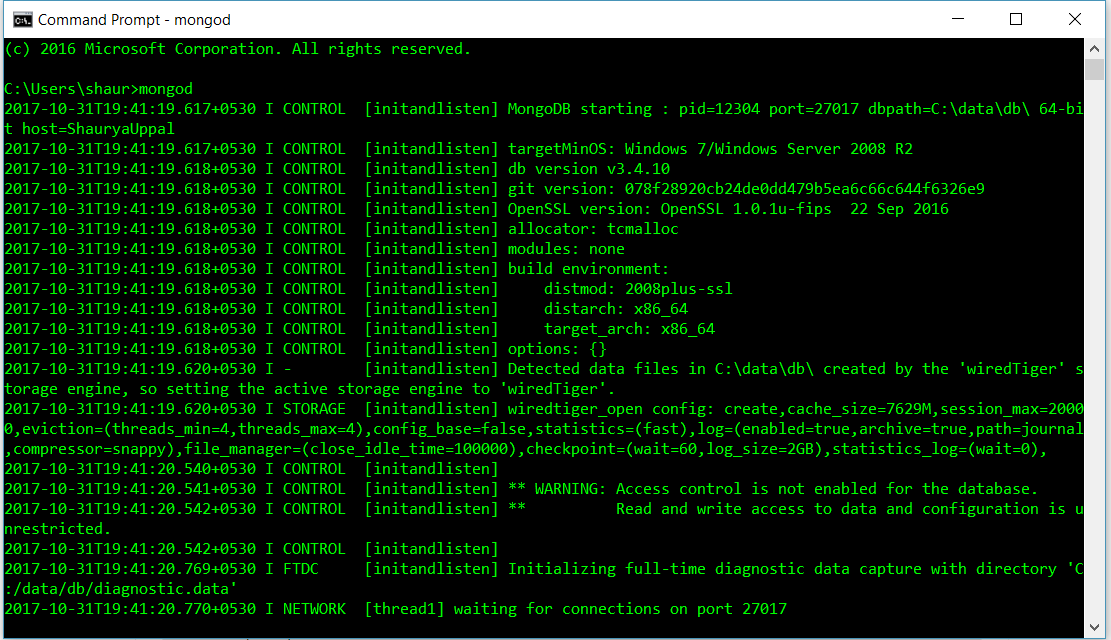 See port number by default is set 27017 (last line in above image).Python has a native library for MongoDB. The name of the available library is “PyMongo”. To import this, execute the following command:
See port number by default is set 27017 (last line in above image).Python has a native library for MongoDB. The name of the available library is “PyMongo”. To import this, execute the following command: